Aluminum: Building for the Future in Desert Environments
Author:Jayminton Time:2024-06-22
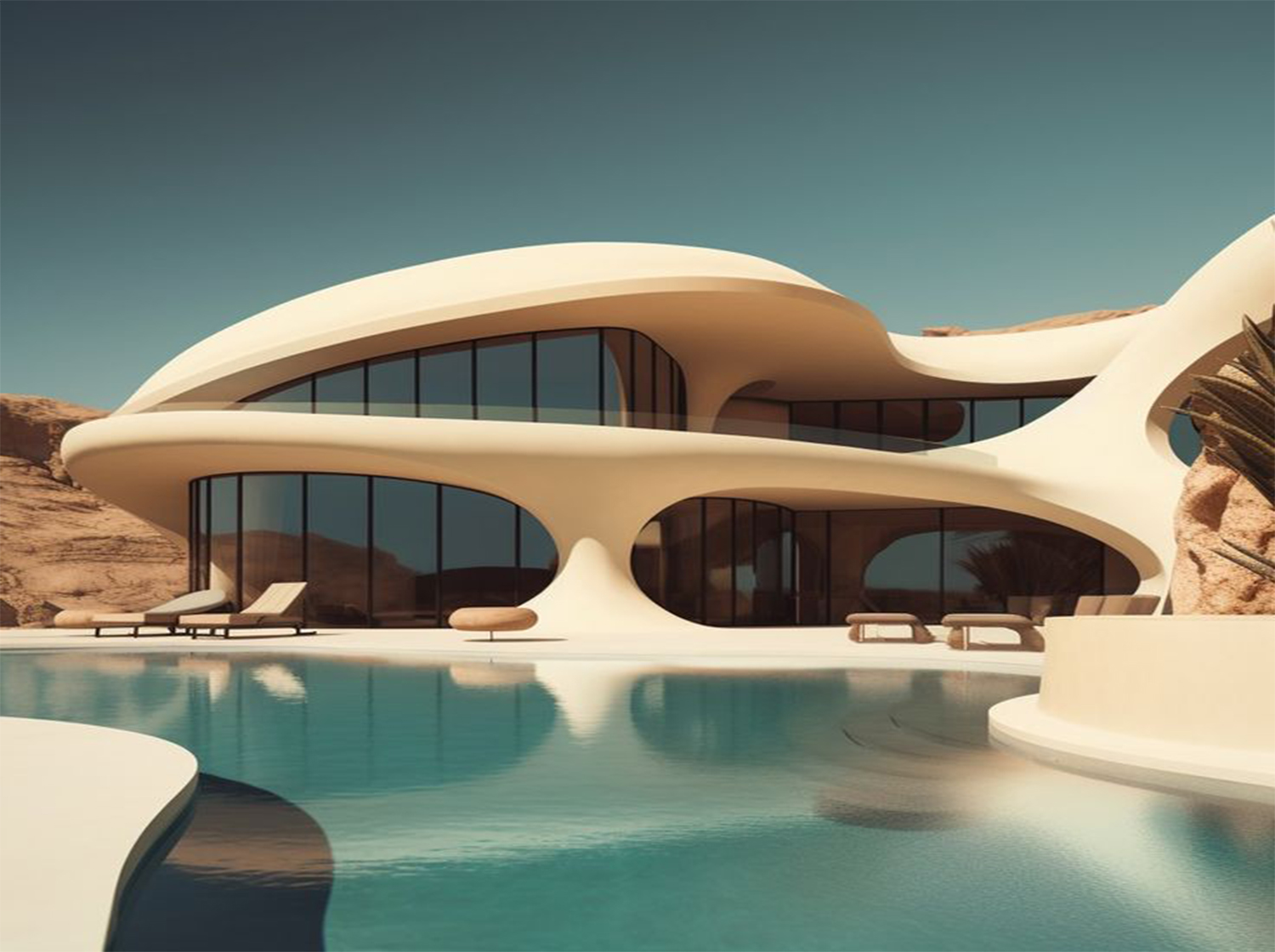

Aluminum has emerged as a transformative material in modern architecture, revolutionizing the way buildings are designed, constructed, and perceived. Its versatility, durability, and aesthetic appeal have made it a favorite among architects worldwide, leading to innovative applications that redefine structural possibilities and sustainability benchmarks.
Versatility and Adaptability
One of aluminum's greatest strengths lies in its versatility. This lightweight yet robust metal can be easily shaped, molded, and manipulated into various forms, allowing architects to create intricate designs and structures that were once considered unachievable. From sleek façades to intricate interior elements, aluminum offers endless possibilities for creative expression without compromising on structural integrity.
Durability and Sustainability
Aluminum's durability is another significant factor driving its popularity in architecture. It is corrosion-resistant and weatherproof, making it ideal for exterior applications where longevity and low maintenance are essential. Its inherent strength-to-weight ratio also contributes to sustainability efforts by reducing the overall material consumption and transportation costs associated with construction projects.
Furthermore, aluminum is highly recyclable, with nearly 75% of all aluminum produced since its discovery still in use today. This recyclability not only minimizes environmental impact but also supports green building initiatives by promoting resource efficiency and reducing carbon footprint throughout the building's lifecycle.
Applications in Modern Architecture
Innovations in aluminum technology have expanded its applications across various facets of modern architecture:
Exterior Facades: aluminum panels and curtain walls provide architects with the flexibility to create visually striking and energy-efficient building envelopes. These systems offer thermal performance enhancements, natural light integration, and aesthetic diversity, contributing to both sustainability and user comfort.
Structural Elements: Aluminum's strength and lightweight nature make it an ideal choice for structural components such as beams, columns, and trusses. This allows for larger spans and taller buildings while reducing the overall load on foundations and support structures.
Interior Design: Aluminum's versatility extends to interior spaces, where it is used for ceiling systems, Wall Cladding, partitions, and furniture. Its ability to be anodized or coated in various colors and textures enhances interior aesthetics while maintaining durability and ease of maintenance.
Sustainable Initiatives: Architects are increasingly integrating aluminum into passive design strategies, such as shading devices and solar panels, to optimize energy efficiency and reduce reliance on artificial heating and cooling systems.
Case Studies
Several iconic buildings around the world showcase the transformative potential of aluminum in architecture:
Burj Khalifa, Dubai: The world's tallest building features aluminum Cladding that enhances its sleek, modern appearance while providing durability against the harsh desert climate.
The Pompidou Centre, Paris: Renowned for its innovative architectural design, this cultural center utilizes aluminum structural elements and exposed mechanical systems as integral parts of its aesthetic expression.
Apple Park, California: Designed with sustainability in mind, the headquarters of Apple Inc. incorporates extensive aluminum elements, including the largest curved glass panels in the world supported by aluminum frames.
Future Directions
Looking ahead, the future of aluminum in architecture appears promising with ongoing advancements in material science and manufacturing techniques. Innovations such as 3D printing of aluminum components, nanotechnology coatings for enhanced durability, and integration with smart building technologies are poised to further expand its applications and sustainability benefits.
In conclusion, aluminum continues to redefine the possibilities of modern architecture through its versatility, durability, and sustainability. As architects and designers explore new frontiers in building design, aluminum remains at the forefront, promising innovative solutions that blend aesthetics with performance and environmental responsibility.
In desert architecture, aluminum finds numerous applications that enhance both functionality and sustainability:
Facade Systems: Aluminum Composite panels or aluminum louvers can be used on building facades to regulate solar heat gain and create visually appealing designs.
Roofing Solutions: Aluminum roofing sheets are durable and lightweight, making them ideal for protecting structures from intense desert sunlight and occasional rain.
Structural Framing: Aluminum's strength-to-weight ratio makes it suitable for structural components like beams and columns, providing stability without adding excessive weight to the building.
Interior Design: Aluminum is also used in interior applications such as partitions, ceilings, and finishes due to its aesthetic appeal and durability.
Case Studies and Innovations
Several notable examples around the world showcase the successful integration of aluminum in desert architecture:
Masdar City, UAE: Known for its sustainable urban development, Masdar City extensively utilizes aluminum in its buildings to maximize energy efficiency and minimize environmental impact.
King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), Saudi Arabia: KAUST features innovative aluminum shading systems that optimize natural light and thermal comfort for its occupants.
Aluminum Domes in Saudi Arabia: Aluminum domes have been used in various projects across Saudi Arabia to create iconic structures that withstand the harsh desert climate while promoting sustainability.
Challenges and Future Directions
While aluminum offers substantial benefits, challenges such as initial costs and energy-intensive production processes remain. However, ongoing research focuses on enhancing the sustainability of aluminum production and exploring new alloys that further improve its performance in extreme environments.
As we look to the future of desert architecture, aluminum stands out as a cornerstone material that enables sustainable, resilient, and aesthetically pleasing building solutions. Its versatility, strength, and environmental benefits make it a vital component in the quest to build smarter and more efficiently in some of the world's harshest climates. Embracing aluminum not only meets the challenges posed by desert environments but also paves the way for a more sustainable future in global construction practices.

 S1 Clip-in Metal ceiling System
S1 Clip-in Metal ceiling System JMT-L4.2 U-Baffle System
JMT-L4.2 U-Baffle System JMT Aluminum Wall Cladding
JMT Aluminum Wall Cladding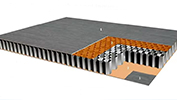 Aluminum Honeycomb Panel
Aluminum Honeycomb Panel Air-Condenser Cover
Air-Condenser Cover Metal Heat Cover
Metal Heat Cover Singapore Changi Airport T2 Arrival
Singapore Changi Airport T2 Arrival Australia Marvrl Stadium City Edge
Australia Marvrl Stadium City Edge Enterprise Information Announcement
Enterprise Information Announcement Construction Industry Solutions
Construction Industry Solutions About Jayminton
About Jayminton Contact US
Contact US