Aluminum Architecture: Pioneering Sustainability in Modern Design
Author:Jayminton Time:2024-06-21
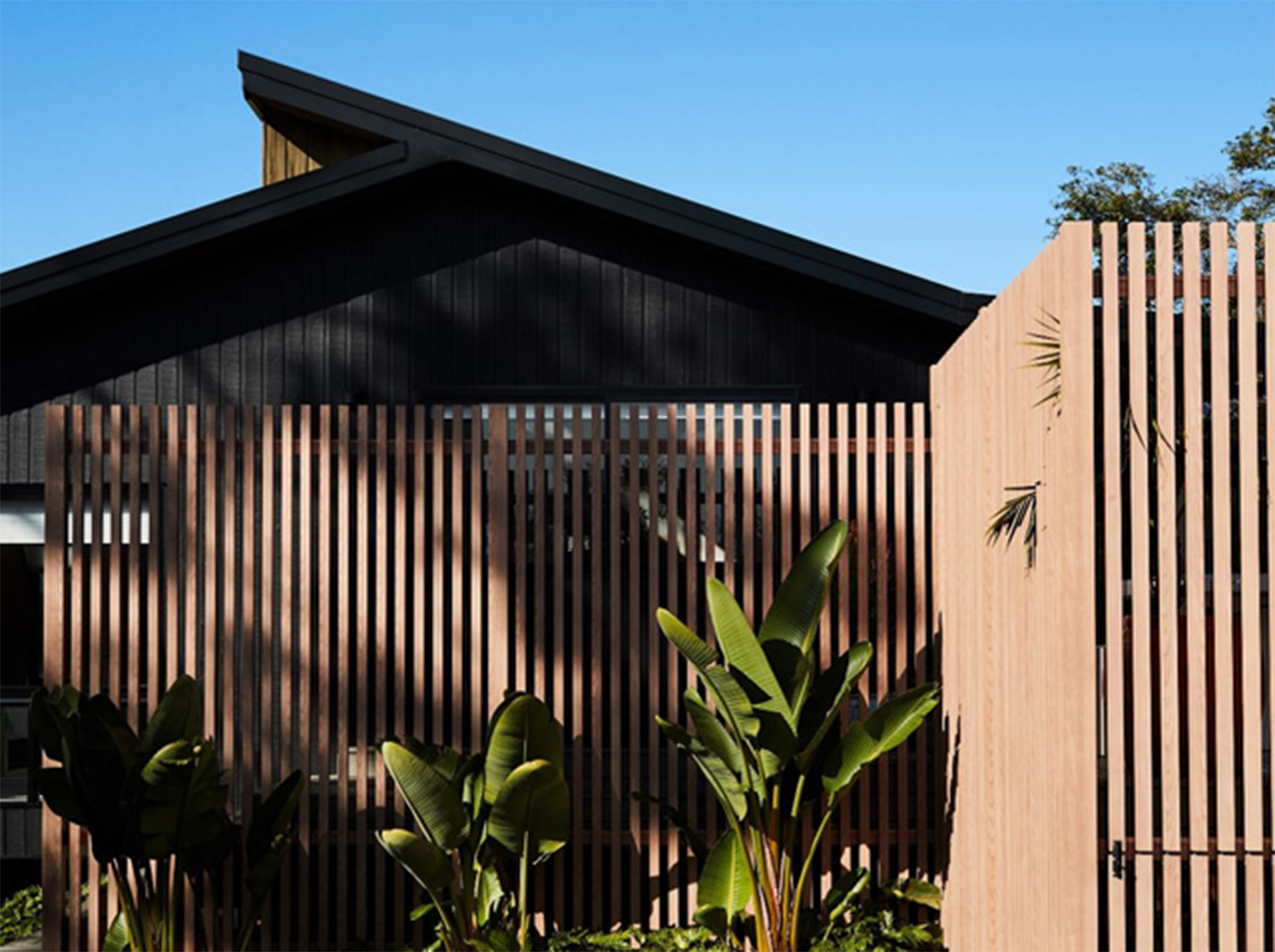

In the ever-evolving field of architecture, sustainability has emerged as a paramount concern, driving innovative approaches to building materials and design. Among these materials, aluminum stands out not only for its aesthetic versatility and structural reliability but also for its significant contributions to environmental sustainability. This article explores the intersection of aluminum and environmental consciousness in architecture, highlighting how this versatile metal is shaping the future of sustainable design.
The Environmental Credentials of Aluminum
Aluminum's sustainability begins with its production process. Unlike many other metals, aluminum is derived from bauxite ore through a process that consumes relatively low energy and emits significantly fewer greenhouse gases. This inherent efficiency translates into a smaller carbon footprint compared to materials like steel or concrete.
Moreover, aluminum is highly recyclable. Up to 75% of all aluminum ever produced is still in use today, a testament to its recyclability and the circular economy it supports. Recycling aluminum requires only a fraction of the energy needed for primary production, making it a preferred choice for environmentally conscious architects and builders.
Design Flexibility and Efficiency
In architectural applications, aluminum offers unparalleled design flexibility. Its strength-to-weight ratio allows for the creation of expansive, lightweight structures that maximize interior space and minimize material usage. This efficiency not only reduces construction costs but also lowers the environmental impact associated with transportation and assembly.
Aluminum's adaptability extends to its aesthetic appeal. Whether used in sleek, modern Facades or integrated into traditional building styles, aluminum can be shaped, textured, and finished to suit virtually any architectural vision. Its ability to withstand corrosion and weathering ensures longevity, maintaining both functionality and visual appeal over time.
Energy Efficiency and Building Performance
Buildings constructed with aluminum components benefit from enhanced energy efficiency. Aluminum's reflective properties can contribute to reduced cooling loads by deflecting solar radiation and minimizing heat gain. This characteristic is particularly valuable in warmer climates, where it helps mitigate the urban heat island effect and lowers overall energy consumption.
Additionally, aluminum's compatibility with advanced building technologies, such as integrated solar panels and smart glazing systems, further enhances building performance. These innovations not only improve energy efficiency but also promote sustainable living practices by reducing reliance on non-renewable energy sources.
Innovative Applications and Future Prospects
The versatility of aluminum continues to inspire innovative architectural solutions worldwide. From iconic skyscrapers to residential dwellings and public infrastructure, architects are increasingly incorporating aluminum into their designs to achieve sustainability goals without compromising on aesthetic appeal or structural integrity.
Looking forward, the integration of aluminum with emerging technologies like 3D printing and digital fabrication promises even greater advancements in sustainable architecture. These technologies enable precise customization and minimize material waste, reinforcing aluminum's role as a cornerstone of environmentally responsible building practices.
Conclusion
Aluminum architecture exemplifies a harmonious blend of sustainability, efficiency, and design innovation in contemporary building practices. As awareness of environmental stewardship grows, the demand for sustainable building materials like aluminum is set to increase. By leveraging its inherent properties and embracing technological advancements, architects and designers can continue to push the boundaries of what is achievable in environmentally friendly architecture, paving the way for a more sustainable built environment for future generations.

 S1 Clip-in Metal ceiling System
S1 Clip-in Metal ceiling System JMT-L4.2 U-Baffle System
JMT-L4.2 U-Baffle System JMT Aluminum Wall Cladding
JMT Aluminum Wall Cladding Aluminum Honeycomb Panel
Aluminum Honeycomb Panel Air-Condenser Cover
Air-Condenser Cover Metal Heat Cover
Metal Heat Cover Singapore Changi Airport T2 Arrival
Singapore Changi Airport T2 Arrival Australia Marvrl Stadium City Edge
Australia Marvrl Stadium City Edge Enterprise Information Announcement
Enterprise Information Announcement Construction Industry Solutions
Construction Industry Solutions About Jayminton
About Jayminton Contact US
Contact US