Aluminum in Architecture: Innovations and Applications
Author:Jayminton Time:2024-06-22
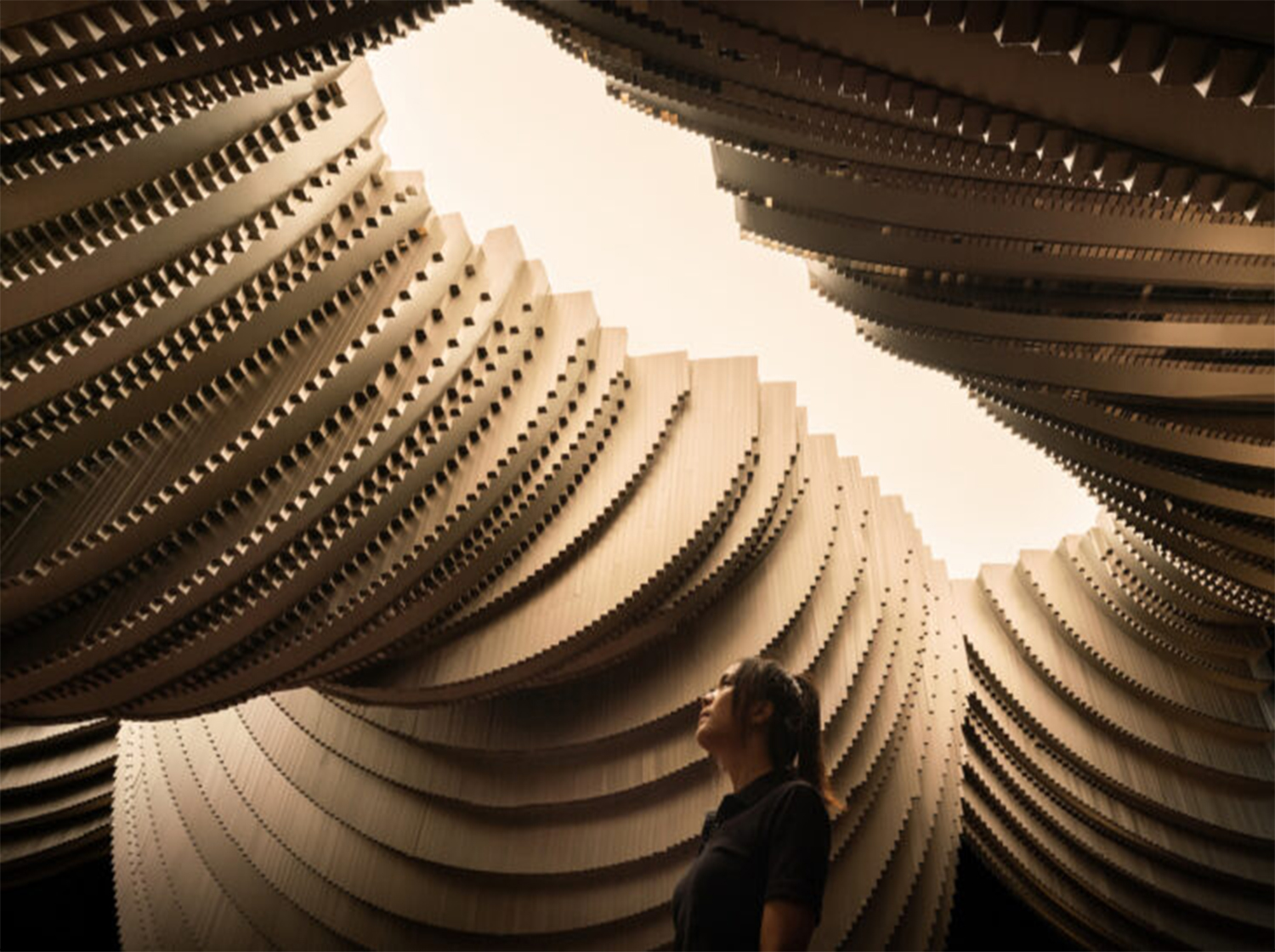

Aluminum, once known primarily for its industrial uses, has increasingly become a cornerstone in modern architectural design. Its unique combination of strength, lightweight properties, and versatility has led to a myriad of innovative applications that have reshaped the way buildings are conceived and constructed worldwide.
Versatility and Design Flexibility
One of aluminum's greatest strengths lies in its versatility. Architects and designers are drawn to its ability to be molded into various shapes and sizes, allowing for intricate and customized designs that would be challenging or impossible with other materials. From sleek, modern Facades to ornate structural elements, aluminum offers unparalleled design flexibility without compromising on durability.
Durability and Sustainability
Aluminum's durability is another key factor driving its popularity in architecture. It is naturally resistant to corrosion and weathering, making it ideal for exterior applications where longevity and minimal maintenance are crucial. Additionally, aluminum is highly recyclable, with nearly all aluminum used in construction projects being recyclable without any loss of quality. This sustainability factor not only reduces environmental impact but also aligns with green building standards and certifications.
Applications in Modern Architecture
The applications of aluminum in modern architecture are diverse and impactful:
Exterior Cladding and Facades: aluminum panels and curtain wall systems are commonly used for building exteriors due to their lightweight nature, ease of installation, and ability to withstand harsh weather conditions. These systems offer thermal insulation properties and can incorporate various finishes and colors to enhance aesthetic appeal.
Structural Components: Aluminum's high strength-to-weight ratio makes it suitable for structural elements such as beams, columns, and roofing systems. This allows architects to design buildings with larger spans and innovative shapes while reducing the overall load on the foundation and support structure.
Interior Design: Within buildings, aluminum is used extensively for interior finishes, partitions, ceilings, and furniture. Its ability to be anodized or coated in different colors and textures provides designers with options to create modern, visually appealing spaces that are also functional and durable.
Sustainable Practices: Architects are increasingly integrating aluminum into sustainable building practices. This includes using aluminum in solar shading devices, energy-efficient windows and doors, and incorporating aluminum alloys that enhance thermal performance and energy efficiency of buildings.
Iconic Examples
Several iconic buildings exemplify the innovative use of aluminum in architecture:
The Guggenheim Museum Bilbao, Spain: Renowned for its titanium-clad exterior, the museum also features aluminum elements in its structural supports and interior finishes, contributing to its distinctive and modern appearance.
The Shard, London: This skyscraper utilizes aluminum curtain wall systems and structural components, combining aesthetics with functionality to create a striking addition to London's skyline.
Petronas Towers, Malaysia: Aluminum Composite panels and cladding systems were used extensively in the construction of these twin towers, showcasing aluminum's durability and design versatility in high-rise buildings.
Future Trends
Looking ahead, the future of aluminum in architecture continues to evolve with advancements in technology and sustainability. Innovations such as nano-coatings for enhanced durability, recycled aluminum alloys, and digital fabrication techniques are pushing the boundaries of what is possible with this versatile material. Additionally, the integration of aluminum with smart building technologies and the adoption of circular economy principles are expected to further enhance its role in sustainable architecture.
In conclusion, aluminum has proven to be a transformative material in modern architecture, offering architects and designers unparalleled versatility, durability, and sustainability. As the industry continues to innovate and push boundaries, aluminum will undoubtedly remain at the forefront of architectural innovation, driving forward the design of buildings that are not only aesthetically stunning but also environmentally responsible and structurally sound.

 S1 Clip-in Metal ceiling System
S1 Clip-in Metal ceiling System JMT-L4.2 U-Baffle System
JMT-L4.2 U-Baffle System JMT Aluminum Wall Cladding
JMT Aluminum Wall Cladding Aluminum Honeycomb Panel
Aluminum Honeycomb Panel Air-Condenser Cover
Air-Condenser Cover Metal Heat Cover
Metal Heat Cover Singapore Changi Airport T2 Arrival
Singapore Changi Airport T2 Arrival Australia Marvrl Stadium City Edge
Australia Marvrl Stadium City Edge Enterprise Information Announcement
Enterprise Information Announcement Construction Industry Solutions
Construction Industry Solutions About Jayminton
About Jayminton Contact US
Contact US