Aluminum in Extreme Environments: Building for the Future
Author:Jayminton Time:2024-07-15
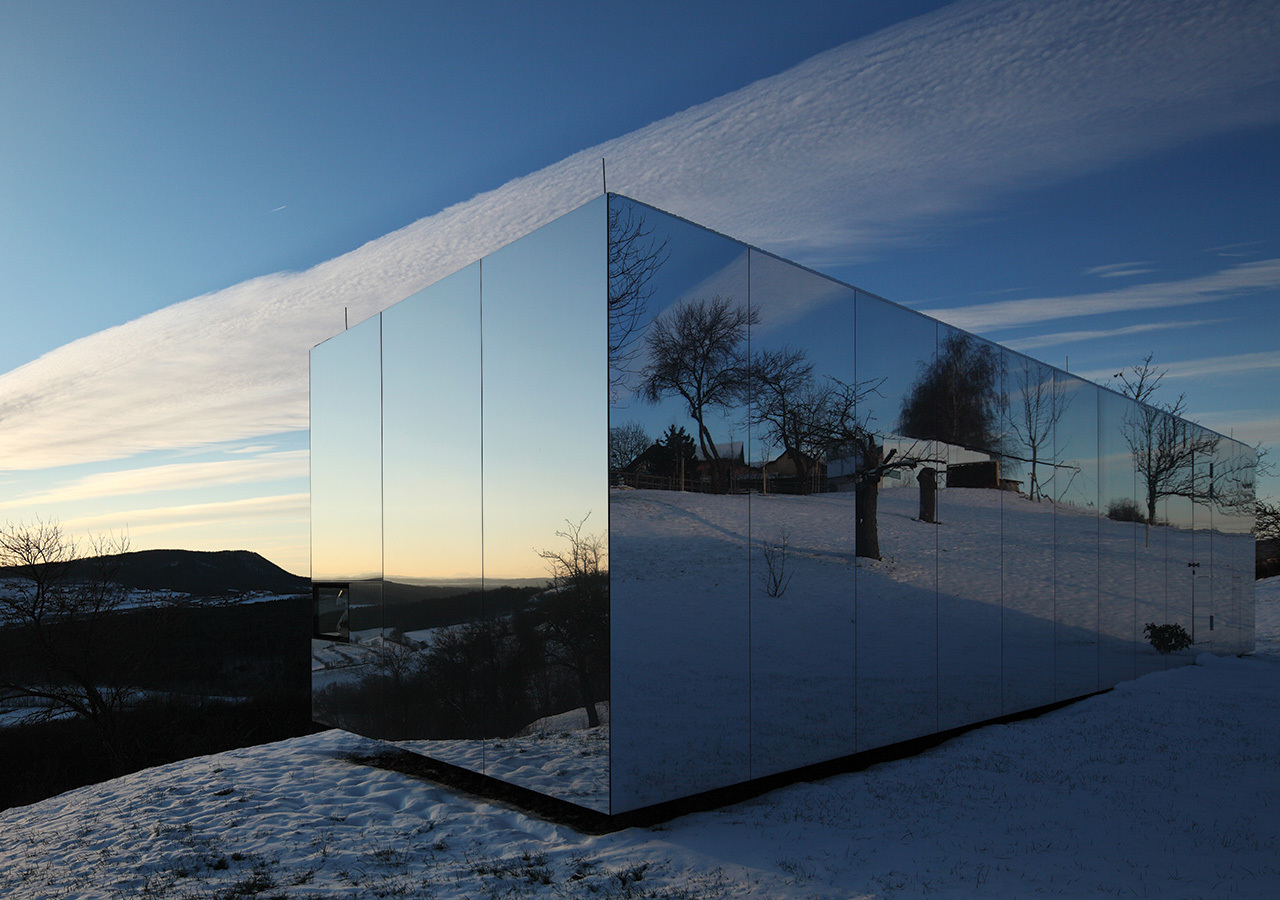
In the realm of modern architecture and construction, the choice of building materials plays a pivotal role in determining the longevity, efficiency, and resilience of structures, especially when faced with extreme environmental conditions. Aluminum, with its unique properties and versatility, has emerged as a frontrunner in constructing buildings that withstand the harshest elements nature can offer.
Understanding Aluminum as a Building Material
Aluminum is a lightweight yet robust metal known for its corrosion resistance, ductility, and recyclability. These characteristics make it highly suitable for a wide range of applications in the construction industry. When engineered and utilized effectively, aluminum contributes significantly to the durability and sustainability of buildings.
Advantages of Aluminum in Extreme Environments
Corrosion Resistance: One of aluminum's most notable qualities is its natural resistance to corrosion. This property is particularly advantageous in coastal or industrial areas where exposure to saltwater or pollutants can compromise other building materials over time. Aluminum's oxide layer acts as a barrier, protecting the metal from rust and deterioration.
Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Despite being lightweight, aluminum exhibits impressive strength and structural integrity. This attribute is crucial in regions prone to high winds, earthquakes, or heavy snow loads. Aluminum structures can withstand these forces while maintaining their stability and safety.
Thermal Performance: Aluminum's thermal conductivity allows for efficient energy management. In extreme climates—whether scorching hot or bitterly cold—aluminum effectively helps regulate indoor temperatures, reducing heating and cooling costs and improving overall energy efficiency.
Design Flexibility: Architects and designers favor aluminum for its flexibility in shaping and forming. It can be extruded, rolled, or cast into various profiles and configurations, offering endless possibilities for innovative and aesthetically pleasing building designs.
Applications in Extreme Environments
High-Temperature Environments: Aluminum's ability to withstand high temperatures without deformation or structural compromise makes it ideal for buildings in desert climates or areas prone to wildfires.
Cold Climates: In regions with prolonged cold spells, aluminum's thermal efficiency and resistance to frost and ice buildup contribute to maintaining interior comfort and structural stability.
Coastal Areas: The coastal environment, with its salty air and high humidity, poses challenges to building materials. Aluminum's corrosion resistance makes it a preferred choice for coastal construction, including beachfront homes, seaside resorts, and maritime infrastructure.
Case Studies and Innovations
Several notable architectural achievements highlight aluminum's effectiveness in extreme environments:
Burj Khalifa, Dubai: The world's tallest building, constructed with aluminum and glass, showcases the metal's ability to withstand high temperatures and strong winds in a desert environment.
Falkirk Wheel, Scotland: This rotating boat lift, featuring aluminum structures, operates in a challenging maritime environment, demonstrating the metal's durability against corrosion and weathering.
Conclusion
Aluminum's exceptional properties make it an invaluable asset in constructing buildings that endure extreme environmental conditions. From its corrosion resistance and structural strength to its thermal performance and design versatility, aluminum continues to redefine the possibilities in modern architecture. As technological advancements and sustainable practices evolve, aluminum remains at the forefront, promising a future where buildings not only withstand but thrive in the face of nature's toughest challenges.

 S1 Clip-in Metal ceiling System
S1 Clip-in Metal ceiling System JMT-L4.2 U-Baffle System
JMT-L4.2 U-Baffle System JMT Aluminum Wall Cladding
JMT Aluminum Wall Cladding Aluminum Honeycomb Panel
Aluminum Honeycomb Panel Air-Condenser Cover
Air-Condenser Cover Metal Heat Cover
Metal Heat Cover Singapore Changi Airport T2 Arrival
Singapore Changi Airport T2 Arrival Australia Marvrl Stadium City Edge
Australia Marvrl Stadium City Edge Enterprise Information Announcement
Enterprise Information Announcement Construction Industry Solutions
Construction Industry Solutions About Jayminton
About Jayminton Contact US
Contact US